When you see an exclamation mark next to the blade server, verify the server hardware
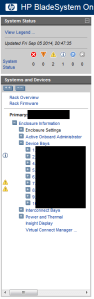
First click on the server device bay and check its status
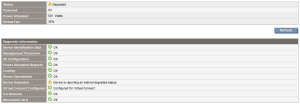
If it shows Device is reporting an internal degraded status, first upgrade the iLO firmware. Then verify if it was solved.
If not, verify if there is a faulty disk in the disk array with hpacucli ctrl all show config
root@linux:~ # hpacucli ctrl all show config
Smart Array P400i in Slot 0 (Embedded) (sn: )
array A (SAS, Unused Space: 0 MB)
logicaldrive 1 (136.7 GB, RAID 1, OK)
physicaldrive 1I:1:1 (port 1I:box 1:bay 1, SAS, 146 GB, OK)
physicaldrive 1I:1:2 (port 1I:box 1:bay 2, SAS, 146 GB, OK)
Install hpasmcli. Part of HP System Health Application and Command Line Utilities (hp-health)
root@linux:/tmp # rpm -ivh hp-health-9.40-1602.37.sles10.x86_64.rpm
Preparing… ########################################### [100%]
1:hp-health ########################################### [100%]
Please read the Licence Agreement for this software at
/opt/hp/hp-health/hp-health.license
By not removing this package, you are accepting the terms
of the “HP Proliant Essentials Software End User License Agreement”.
Using Proliant Standard
IPMI based System Health Monitor
Using standard Linux IPMI device driver
Starting ipmi drivers: done
Starting Proliant Standard
IPMI based System Health Monitor (hpasmlited):
done
Starting HP Advanced Server Recovery Daemon done
The hp-health RPM has installed successfully.
Start hpasmcli
root@linux:~ # hpasmcli
HP management CLI for Linux (v2.0)
Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Group, L.P.
————————————————————————–
NOTE: Some hpasmcli commands may not be supported on all Proliant servers.
Type ‘help’ to get a list of all top level commands.
————————————————————————–
Another component that usually gives problem is a Memory DIMM.
hpasmcli> show dimm
DIMM Configuration
——————
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 1
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 2
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 3
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 4
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 5
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 6
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: DIMM is degraded
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 7
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 8
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 9
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 10
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 11
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 12
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 13
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 14
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 15
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
Cartridge #: 0
Module #: 16
Present: Yes
Form Factor: fh
Memory Type: OTHER(14h)
Size: 4096 MB
Speed: 667 MHz
Supports Lock Step: No
Configured for Lock Step: No
Status: Ok
hpasmcli>
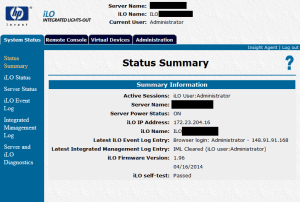
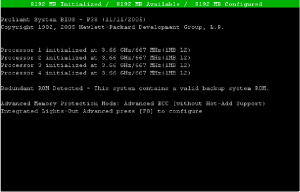
After this, you’ll have to run diagnostics using HP Insight Online Diagnostics that you installed on the operating system or boot with the CD/DVD to run the HP Insight Offline Diagnostics






You must be logged in to post a comment.